Increase in Basic Personal Amount (BPA)
The federal basic personal amount will increase to $16,129 in 2025. For individuals with incomes exceeding $177,788, the additional BPA will gradually decrease, and for those with incomes above $253,414, the additional BPA will reduce to $0. Their BPA will then be $14,538. In Ontario, the BPA is set at $12,747.
CPP Contribution Rates
The Canada Pension Plan (CPP) contribution rate will remain at 5.95% for both employees and employers in 2025. The maximum annual contribution for individuals will be $4,034.10, and for self-employed individuals, $8,068.20. The Year’s Maximum Pensionable Earnings (YMPE) will be $71,300. Additionally, a second contribution rate and income ceiling (YAMPE) will apply to earnings between $71,300 and $81,200. Employees and employers will contribute at a 4% rate for this portion, with a maximum contribution of $396 each. For self-employed individuals, the rate will be 8%, with a maximum contribution of $792.
Reduction in EI Premium Rate
Employment Insurance (EI) premium rates will decrease from 1.66% in 2024 to 1.64% in 2025. The maximum annual EI contribution will be $1,077.48, based on Maximum Annual Insurable Earnings of $65,700.
TFSA and RRSP Contribution Limits
The Tax-Free Savings Account (TFSA) contribution limit for 2025 remains at $7,000, with a cumulative maximum contribution limit of $102,000. The maximum annual contribution limit for Registered Retirement Savings Plans (RRSPs) will be $32,490.
New Capital Gains Inclusion Rate
The federal budget for 2024 proposed increasing the capital gains inclusion rate from 50% to 66% for individuals with annual capital gains exceeding $250,000. Corporations and trusts will also see their capital gains inclusion rate rise to two-thirds from the previous 50%. Although this change has yet to pass Parliament, the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) has been temporarily enforcing the measure since June 25, pending legislation or a change in government policy.
Small Business Tax Rates
There are minimal changes to small business income tax rates. The federal small business tax rate for active business income up to $500,000 remains at 9%. Ontario’s small business tax rate is 3.2%, leading to a combined rate of 12.2%. However, with the additional CPP contributions, businesses will face increased costs. Small business owners may consider increasing dividends, though personal and family situations should be evaluated, and professional advice is recommended. The most significant corporate tax change is the increase in the capital gains inclusion rate to two-thirds.
Canadian Entrepreneurs Incentive Program
Another policy being implemented by CRA but not yet legislated is the Canadian Entrepreneurs Incentive Program. It reduces the taxable portion of lifetime capital gains for Canadian-Controlled Private Corporation (CCPC) owners up to $2 million to one-third. This program will phase in starting in 2025, with annual increases of $400,000, reaching $2 million by 2029. Tax experts note that these changes complicate capital gains taxation, especially regarding business equity appreciation.
Summary
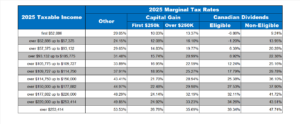
The 2025 tax reforms are diverse, with changes like the capital gains inclusion rate having significant impacts on individuals and businesses. It’s advised to align financial plans with these new policies and work with professionals to minimize burdens. Below is a chart of Ontario’s personal tax rates for 2025 for reference.